Detection and Severity Assessment of Parkinson’s Disease by Analysis of Wearable Sensors Data Using Gramian Angular Fields and Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
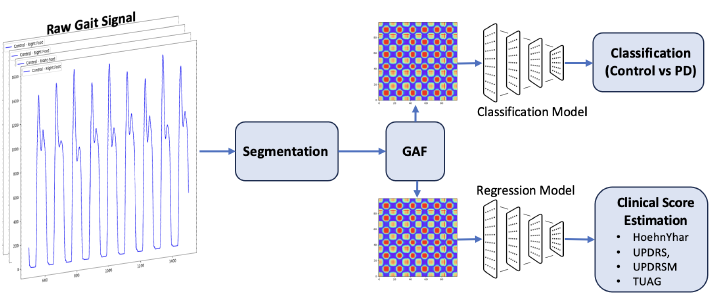
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is the second-most common neurodegenerative disease. It affects millions of individuals worldwide, and is most prevalent in the elderly population, with more than 20,000 new diagnosed cases each year. PD is a progressive neurodegenrative condition which confers significant morbidity especially in the advanced stages of the disease. The current clinical methods for diagnosis and severity assessment of PD rely on visual and physical examination of subjects and look for identification of key disease motor signs and symptoms such as bradykinesia, rigidity, tremor, and postural instability. Identification of more quantitative approaches to assess diagnosis and prognisis could improve treatment for PD patients. In the present study, we develop a method for diagnosis and severity assessment of PD using a model based on Gramian Angular Fields in combination with deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) applied to PD gait signals captured using pressure sensors embedded into insoles. We achieved an accuracy of 98.6%, TPR of 99.2%, TNR of 98.5% and ROC area under curve = 1.0, indicating superior classification performance for PD diagnosis compared to recent studies in the literature, while providing visual representations on differences between normal and PD gait patterns. Estimation of disease severity scores using gait signals was accurate for Hoehn & Yahr scale and Timed Up and go time (R2 > 0.8), while we achieved lower prediction performance for UPDRS and UPDRSM scores (R2 < 0.2). These results were achieved using gait signals recorded in time windows as small as 10 seconds, which may pave the way for shorter, more accessible assessment tools for diagnosis and severity assessment of PD.