Assessing the quality of reporting in artificial intelligence/machine learning research for cardiac amyloidosis
Abstract
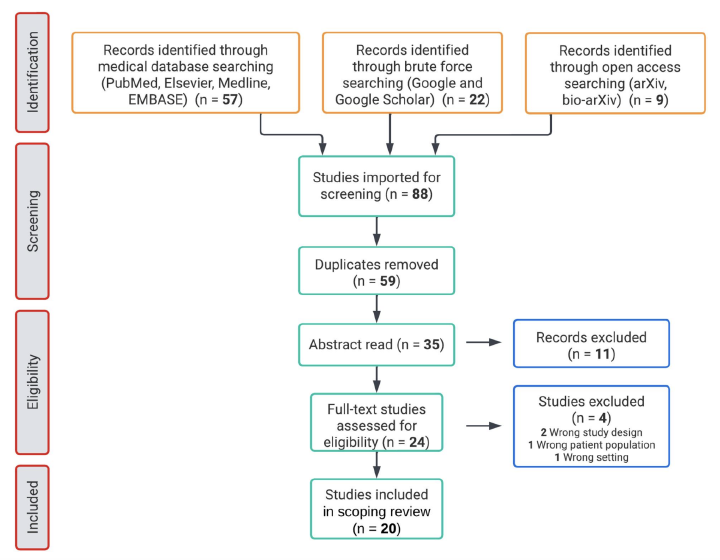
Objectives: Despite the rapid development of AI in clinical medicine, reproducibility and methodological limitations hinder its clinical utility. In response, MINimum Information for Medical AI Reporting (MINIMAR) standards were introduced to enhance publication standards and reduce bias, but their application remains unexplored. In this review, we sought to assesses the quality of reporting in AI/ML studies of cardiac amyloidosis (CA) an increasingly important cause of heart failure. Materials and Methods: Using PRISMA-ScR guidelines, we performed a scoping review of English-language articles published through May 2023 which applied AI/ML techniques to diagnose or predict CA. Non-CA studies and those with selective feature sets were excluded. Two researchers independently screened and extracted data. In all, 20 studies met criteria and were assessed for adherence to MINIMAR standards. Results: The studies showed variable compliance with MINIMAR. Most reported participant age (90%) and gender (85%), but only 25% included ethnic or racial data, and none provided socioeconomic details. The majority (95%) developed diagnostic models, yet only 85% clearly described training features, and 20% addressed missing data. Model evaluation revealed gaps; 80% reported internal validation, but only 20% conducted external validation. Discussion and Conclusion: This study, one of the first to apply MINIMAR criteria to ML research in CA, reveals significant variability and deficiencies in reporting, particularly in patient demographics, model architecture, and evaluation. These findings underscore the need for stricter adherence to standardized reporting guidelines to enhance the reliability, generalizability, and clinical applicability of ML/AI models in CA..