Enhancing Metabolic Syndrome Prediction with Hybrid Data Balancing and Counterfactuals
Abstract
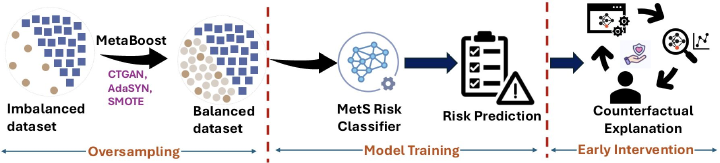
Metabolic Syndrome (MetS) is a cluster of interrelated risk factors that significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes. Despite its global prevalence, accurate prediction of MetS remains challenging due to issues such as class imbalance, data scarcity, and methodological inconsistencies in existing studies. In this paper, we address these challenges by systematically evaluating and optimizing machine learning (ML) models for MetS prediction, leveraging advanced data balancing techniques and counterfactual analysis. Multiple ML models, including XGBoost, Random Forest, TabNet, etc., were trained and compared under various data balancing techniques such as random oversampling (ROS), SMOTE, ADASYN, and CTGAN. Additionally, we introduce MetaBoost, a novel hybrid framework that integrates SMOTE, ADASYN, and CTGAN, optimizing synthetic data generation through weighted averaging and iterative weight tuning to enhance the model’s performance (achieving up to a 1.87% accuracy improvement over individual balancing techniques). A comprehensive counterfactual analysis is conducted to quantify the feature-level changes required to shift individuals from high-risk to low-risk categories. The results indicate that blood glucose (50.3%) and triglycerides (46.7%) were the most frequently modified features, highlighting their clinical significance in MetS risk reduction. Additionally, probabilistic analysis shows elevated blood glucose (85.5% likelihood) and triglycerides (74.9% posterior probability) as the strongest predictors. This study not only advances the methodological rigor of MetS prediction but also provides actionable insights for clinicians and researchers, highlighting the potential of ML in mitigating the public health burden of metabolic syndrome.