Knowledge-Infused LLM-Powered Conversational Health Agent - A Case Study for Diabetes Patients
Abstract
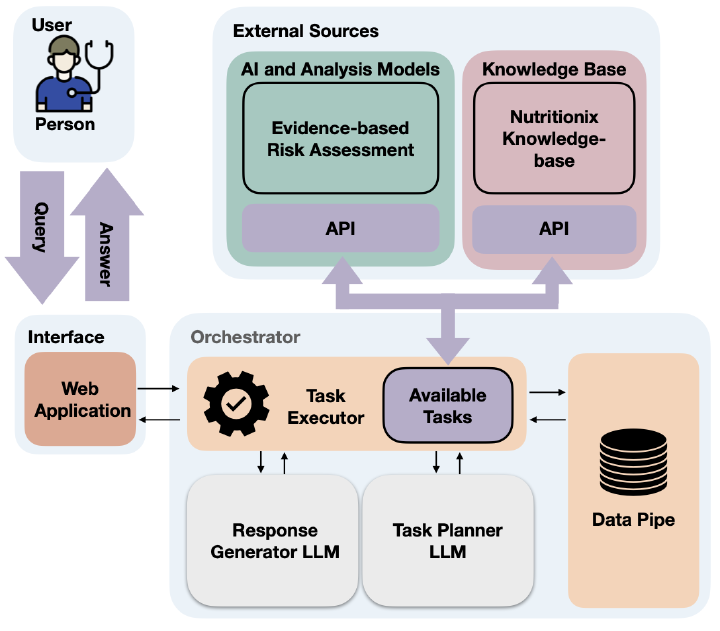
Effective diabetes management is crucial for maintaining health in diabetic patients. Large Language Models (LLMs) have opened new avenues for diabetes management, facilitating their efficacy. However, current LLM-based approaches are limited by their dependence on general sources and lack of integration with domain-specific knowledge, leading to inaccurate responses. In this paper, we propose a knowledge-infused LLMpowered conversational health agent (CHA) for diabetic patients. We customize and leverage the open-source openCHA framework, enhancing our CHA with external knowledge and analytical capabilities. This integration involves two key components 1) incorporating the American Diabetes Association dietary guidelines and the Nutritionix information and 2) deploying analytical tools that enable nutritional intake calculation and comparison with the guidelines. We compare the proposed CHA with GPT4. Our evaluation includes 100 diabetes-related questions on daily meal choices and assessing the potential risks associated with the suggested diet. Our findings show that the proposed agent demonstrates superior performance in generating responses to manage essential nutrients.