On-Device Machine Learning for Diagnosis of Parkinson's Disease from Hand Drawn Artifacts
Abstract
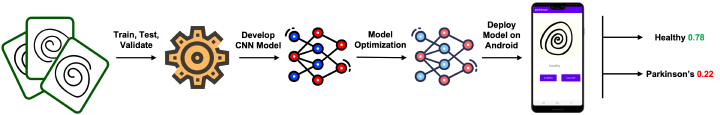
Effective diagnosis of neuro-degenerative diseases is critical in providing early treatments, which in turn can lead to substantial savings in medical costs. Machine learning models can help with the diagnosis of such diseases like Parkinson’s and aid in assessing disease symptoms. This work introduces a novel system that integrates pervasive computing, mobile sensing, and machine learning to classify hand-drawn images and provide diagnostic insights for screening of Parkinson’s disease patients. We design a computational framework that combines data augmentation techniques with optimized convolutional neural network design for on-device and real-time image classification. We assess the performance of the proposed system using two datasets of images of Archimedean spirals drawn by hand and demonstrate that our approach achieves 76% and 83% accuracy respectively. Thanks to 4x memory reduction via integer quantization, our system can run fast on an Android smartphone. Our study demonstrates that pervasive computing may offer an inexpensive and effective tool for early diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease.