Edge AI
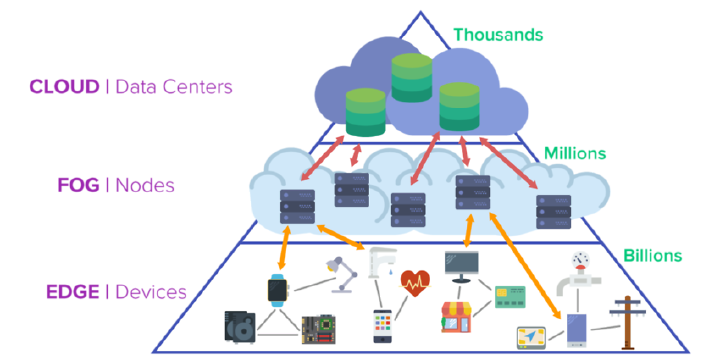
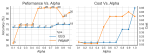
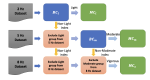
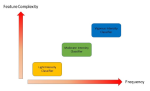
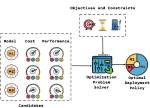
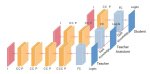
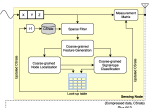
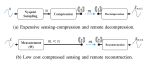
The stringent constrained resources available on tiny sensor nodes introduce a number of challenges regarding accuracy, power-efficiency, user-comfort, and security. These design considerations, however, often impose conflicting requirements. Thus, a comprehensive research approach to design future medical embedded systems and corresponding optimizations at different levels must consider these interdependent and conflicting requirements. We research methods of optimizing medical embedded systems for power-efficiency while taking into account other performance metrics. The goal is to develop tools, methodologies, and algorithms towards comprehensive approaches to address cross-layer optimization issues related to power, performance, user-comfort, and security.
Embedded Machine Intelligence Lab
Research Lab
The current focus of our research in the Embedded Machine Intelligence Lab (EMIL) is on design, development, and validation of algorithms, tools, and technologies that enhance utilization and large-scale adoption of digital health systems. To validate and refine the new technology, we actively collaborative with domain experts, community stakeholders, and end-users. This end-to-end approach results in innovative, evidence-based and cost-conscious health solutions for individuals and care providers.